非编码RNA(Non-coding RNA)是指不编码蛋白质的RNA。其中包括rRNA、tRNA、snRNA、snoRNA 、microRNA 和lncRNA等多种已知功能的 RNA,还包括未知功能的RNA。
长链非编码RNA(long noncoding RNA,lncRNA)是一类长度>200bp的RNA,由RNA聚合酶Ⅱ转录,lncRNA具有保守的二级结构,大部分不编码蛋白质。LncRNA发挥功能的方式很广,可以与蛋白、DNA和RNA相互作用,参与多种生物学过程的调控。主要包括基因组表观遗传修饰、调控转录后翻译、发挥ceRNA、增强子RNA作用等,从而对细胞的增殖、分化、迁移、凋亡、免疫等发挥调控作用。
金开瑞提供的非编码RNA服务:miRNA、lncRNA、tRFs
研究方案(以lncRNA为例)
1、采用二代测序或芯片技术找出不同组样本差异表达的lncRNA
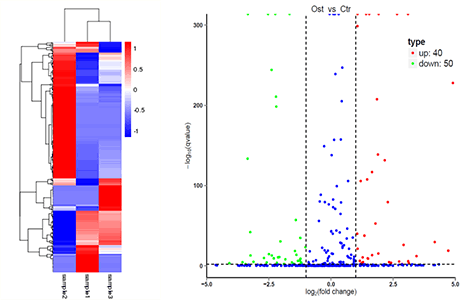
图1. LncRNA 差异表达聚类结果及差异表达火山图
2、lncRNA/miRNA筛选验证
采用RT-PCR或者qRT-PCR检测lncRNA/miRNA在不同组织和细胞中的表达水平。
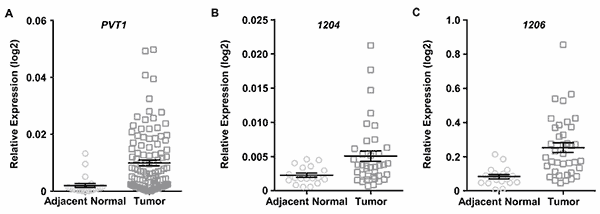
图2. PVT1和 miRNA在宫颈癌组织中的表达
(Iden, M.et al.The lncRNA PVT1 Contributes to the Cervical Cancer Phenotype and Associates with Poor Patient Prognosis.PloS one.2016.May 27;11(5))
3、细胞系鉴定
采用对肝癌细胞(如hepG2、hep3b、huh7)STR位点和Amelogenin位点的基因分型技术,进行细胞鉴定。
| Marker | 细胞库信息 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allele1 | Allele2 | Allele3 | Allele1 | Allele2 | Allele3 | |
| D5s818 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | ||
| D13s317 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 14 | ||
| D7s820 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 14 | ||
| D16s539 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | ||
| VWA | 16 | 18 | 17 | 17 | ||
| TH01 | 7 | 7 | 6 | 7 | ||
| AMEL | X | X | X | X | ||
| TPOX | 8 | 11 | 9 | 9 | ||
| CSF1PO | 11 | 11 | 8 | 8 | ||
| D21S11 | 30 | 30 | ||||
4、lncRNA功能及下游靶标分子研究
4.1、构建lncRNA/miRNA的过表达(基因敲除)稳转癌细胞株;
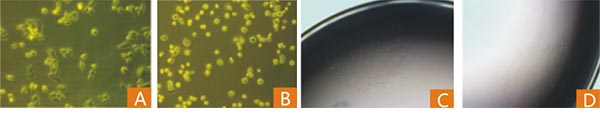
图3. 基因过表达/敲除后单克隆细胞株的筛选
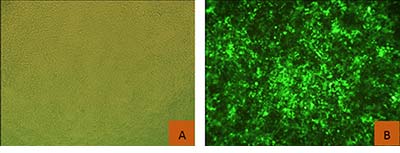
图4. CRISPR/Cas9和慢病毒稳定细胞系
4.2、MTT/CCK8法测定细胞生长活力;
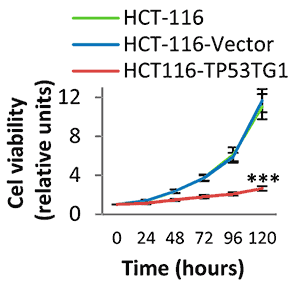
图5. 转染TP53TG1 减少了细胞的活力
(Diaz-Lagares A, et al.Epigenetic inactivation of the p53-induced long noncoding RNA TP53 target 1 in human cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Nov 22;113(47):E7535-E7544.)
4.3、流式细胞检测细胞凋亡;
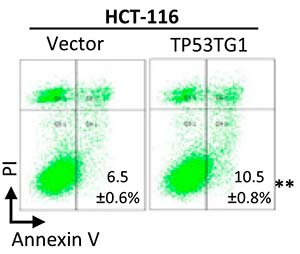
图6. HCT-116 cells 稳定转染TP53TG1 24小时后检测细胞的凋亡率
(Diaz-Lagares A, et al.Epigenetic inactivation of the p53-induced long noncoding RNA TP53 target 1 in human cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Nov 22;113(47):E7535-E7544.)
4.4、软琼脂克隆形成实验;
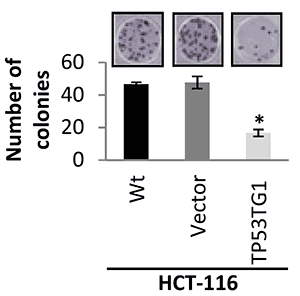
图7. TP53TG1 抑制了HCT-116细胞的克隆形成
(Diaz-Lagares A, et al.Epigenetic inactivation of the p53-induced long noncoding RNA TP53 target 1 in human cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Nov 22;113(47):E7535-E7544.)
4.5、细胞划痕实验;
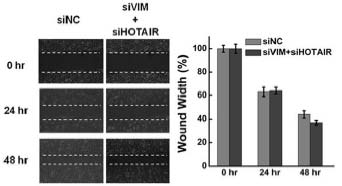
图8. 伤痕愈合实验检测 VIM 敲低和过表达对细胞侵袭力的影响
(Peng Zheng,Quantitative Proteomics Analysis Reveals Novel Insights into Mechanisms of Action of Long Non-coding RNA HOTAIR in Hela Cells.MCP. 2015.)
4.6、细胞体外Matrigel侵袭实验;
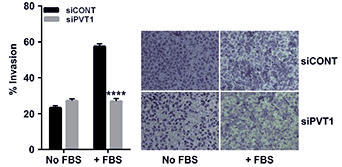
图9. 与siCONT细胞相比,siPVT1细胞侵袭力明显降低
(Iden, M.et al.The lncRNA PVT1 Contributes to the Cervical Cancer Phenotype and Associates with Poor Patient Prognosis.PloS one.2016.May 27;11(5))
4.7、Western blot检测肿瘤相关蛋白表达。
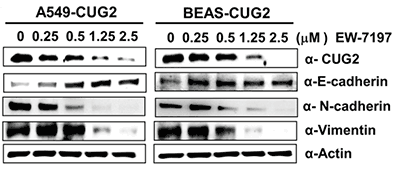
图10. 用不同浓度的EW-7197 (0.25, 0.5, 1.25 and 2.5 μM) 处理A549-CUG2 and BEAS-CUG2 细胞24 h。免疫印迹检测 CUG2, E-cadherin, N-cadherin, and vimentin 的表达
(Kaowinn S, Kim J, Lee J, Shin DH, et, al. Cancer upregulated gene 2 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human lung cancer cells via TGF-β signaling. Oncotarget. 2016 Dec
5、蛋白质组学寻找调控的下游靶标分子
应用蛋白质组学iTRAQ(SILAC,SWATH)定量方法和生物信息学找到lncRNA/miRNA调控的靶标。
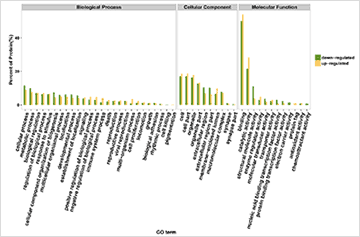
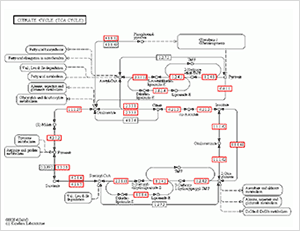
图11. 蛋白质组学ITRAQ/SWATH 和差异蛋白通路分析
6、采用FISH技术研究lncRNA在细胞中定位分布
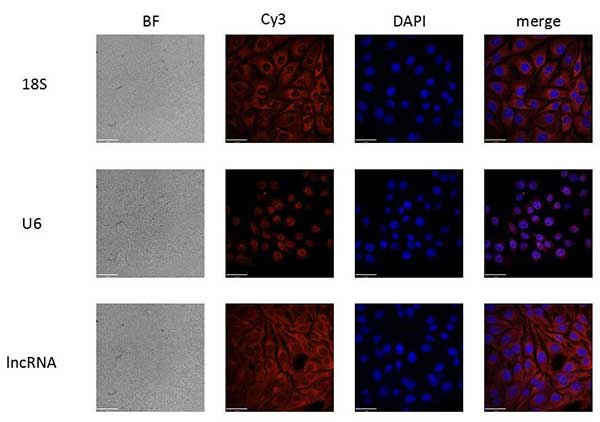
图12. 目的lncRNA在细胞中的位置分布(18S和U6为内参)
7、lncRNA作用机制研究
7.1、采用体外转录技术,RNA pull down, LC- MS等技术手段检测与RNA互作的蛋白质。

图13. RNA pull down后质谱鉴定、WB检测
7.2、RIP验证与蛋白质结合的lncRNA或者lncRNA与miRNA的互作

图14. AP-1蛋白与RNA的相互作用RIP
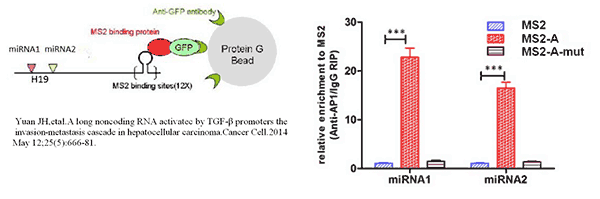
图15. MS2- RIP实验原理图(表达Lnc-A的质粒富集miRNA1miRNA2的效率比不表达Lnc-A的MS2组明显提高。通过对照,说明MS2-A可以与miRNA1和miRNA2相互结合)
7.3、双荧光素酶基因检测miRNA和lncRNA/mRNA的互作情况
生物信息学预测分析

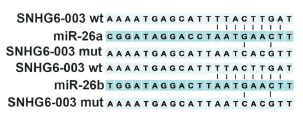
图16. 利用生物信息学方法预测lncRNA与miRNA的结合位点
双荧光素酶和RIP验证
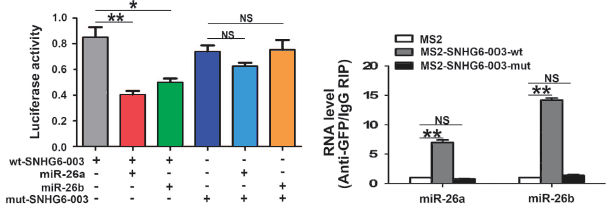
图17. 双荧光素酶和RIP验证lncRNA可以与miR-26a结合
(C Cao, Zhang T, Zhang D, et al.The long non-coding RNA, SNHG6-003, functions as a competing endogenous RNA to promote the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 2017 Feb 23;36(8):1112-1122. )
8、动物实验
8.1、成瘤模型

图18. 肝癌裸鼠成瘤模型,通过活体成像和测量观察不同处理小鼠肿瘤的生长、转移情况
(C Cao, Zhang T, Zhang D, et al.The long non-coding RNA, SNHG6-003, functions as a competing endogenous RNA to promote the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 2017 Feb 23;36(8):1112-1122. )
8.2、普通药物模型或基因治疗模型
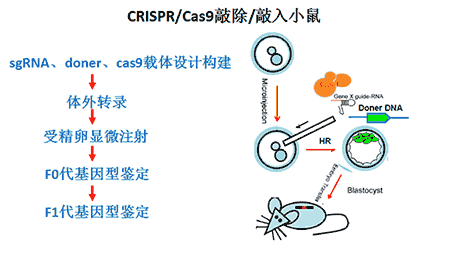
8.3、模式动物:CRISPR/Cas9敲除或敲入的模式动物
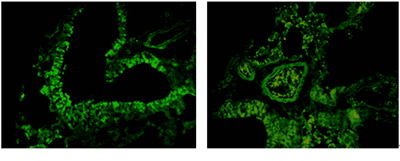
图19. 腺病毒注射小鼠尾静脉后,隔一段时间通过肺组织切片观察某基因对肺的影响
8.4、损伤修复模型
如骨断裂恢复模型
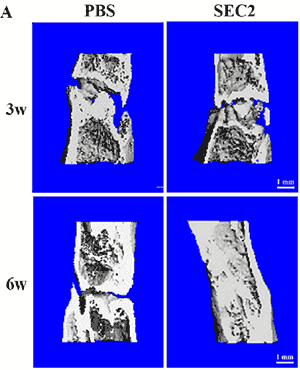
图20. 小鼠骨断裂后用SEC2处理,X-ray拍摄结果显示SEC2组小鼠恢复更快
(Xu J, Wu T, Sun Y, et al.Staphylococcal Enterotoxin C2 Expedites Bone Consolidation in Distraction Osteogenesis. J Orthop Res. 2017 Jun;35(6):1215-1225. )
参考文献
1、Budhu A, Forgues M, Ye QH, et al. Prediction of venous metastases, recurrence, and prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma based on a unique immune response signature of the liver microenvironment. Cancer Cell. 2006 Aug;10(2):99-111.
2、Fidler IJ. The pathogenesis of cancer metastasis: the 'seed and soil' hypothesis revisited. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003 Jun;3(6):453-8.
3、Ocaña OH, Córcoles R, Fabra A, et al. Metastatic colonization requires the repression of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition inducer Prrx1. Cancer Cell. 2012 Dec 11;22(6):709-24.
4、Massagué J. TGFbeta in Cancer. Cell. 2008 Jul 25;134(2):215-30.
5、Faghihi MA, Modarresi F, Khalil AM, et al. Expression of a noncoding RNA is elevated in Alzheimer's disease and drives rapid feed-forward regulation of beta-secretase. Nat Med. 2008 Jul;14(7):723-30.